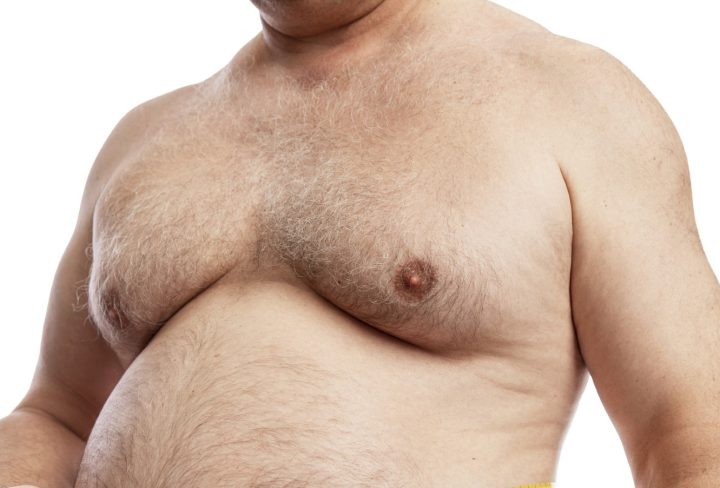
Gynecomastia is a common condition in men in which the breasts grow unevenly enlarged and overdevelop than usual. This often occurs during the puberty stage where there is hormonal imbalance. This is also seen in new-born babies and in men as they age.
The procedure may include liposuction, excision (using larger incisions) or a combination of both the procedures. This procedure is recommended to improve self-confidence, enhance their appearance, and reduce discomfort that can result from larger breasts.
Symptoms of Gynecomastia
Most adult men with gynecomastia report no symptoms. However, the common symptoms of may include:
- Pain and swollen breast tissue
- Breast tenderness
- Fatty tissue beneath the nipple
- Nipple sensitivity with rubbing against clothes
When to See a doctor?
See your doctor if you have:
- Swelling
- Pain or tenderness
- Nipple discharge from the breasts
Gynecomastia Risk Factors
Risk factors for gynecomastia include:
- Adolescence
- Older age
- Use of anabolic steroids to enhance athletic performance
- Certain health conditions (liver and kidney disease, thyroid disease, hormonally active tumors, and Klinefelter syndrome)
Gynecomastia Causes
An imbalance between hormones (estrogen and androgen) typically causes gynecomastia. Men’s bodies usually produce small amounts of estrogen, the hormone that controls breast growth. If the body produces more amounts of estrogen, or you have low testosterone (hypogonadism), the breasts may enlarge.
Sometimes people with obesity develop enlarged breasts due to excess fatty tissue. This condition is known as pseudo gynecomastia.
The health conditions that cause gynecomastia includes:
- Adrenal tumors
- Alcohol consumption
- Kidney, thyroid, and liver disease
- Klinefelter syndrome (an inherited condition)
Diagnosis of Gynecomastia
Your doctor will assess symptoms, perform a physical exam, and review your medical and family history. To check the hormone levels your doctor might order a blood test.
To rule the other causes your doctor may order tests such as:
- Breast ultrasound to view detailed images of breast growths.
- Mammogram to examine unusual growths or changes in breast tissue.
Complications of Gynecomastia
Men with gynecomastia have a slightly higher risk of breast cancer. You should see your doctor anytime you feel or notice abnormal breast changes.
Gynecomastia Treatment
Gynecomastia usually resolves over time without treatment or surgery. However, if gynecomastia is caused by an underlying condition (hypogonadism, malnutrition, or cirrhosis) that underlying condition may need treatment.
Treatment with medication (Tamoxifen, Aromatase inhibitors) may be necessary if gynecomastia does not improve on its own or if it causes significant pain, tenderness, or embarrassment.
If enlarged breasts are significant and bothersome even after initial treatment or observation, your doctor may advise surgery.
Gynecomastia Surgery
- Liposuction: This type of surgery removes breast fat but not the breast gland tissue itself.
- Mastectomy: This type of surgery removes the breast gland tissue. The surgery is often performed using only small incisions. It is less invasive and involves less recovery time.
Surgeons usually use only liposuction to remove breast tissue. A suction is inserted through the tiny incisions or cuts to remove the fat tissue.
If there is excess skin, fat and tissue, your doctor may recommend excision. This technique uses larger incisions to remove breast tissue. Your provider can also reposition your nipple and areola during the excision procedure. The incision patterns, lengths and locations depend on the size of your breasts and desired aesthetic look you want.
For both the techniques general anesthesia is administered through a vein in your arm. You will be asleep throughout the procedure, and you will not feel pain or discomfort during the procedure.
Recovery Care for Gynecomastia Surgery
- During the first few days you might feel little tenderness or soreness. The discomfort gets better within in a week.
- You can resume back to normal routine after 2 weeks of the surgery.
- While you are healing, follow your doctor’s instructions carefully.
- Refrain from lifting or carrying anything heavy and reaching your arms above your head.
The results will be evident after three to six months following surgery. It takes time for your breast tissue to heal and for swelling to decrease. However, the results are permanent.
Prevention for Gynecomastia
You cannot prevent the hormonal changes that cause gynecomastia. However, you can reduce your risk of breast enlargement by switching medications or seeking treatment for a substance use disorder.
- Avoid using drugs (anabolic steroids, amphetamines, heroin, and marijuana).
- Do not drink alcohol. If you do drink, do so in moderation.
Conclusion
Gynecomastia, commonly known as “man boobs,” is a common condition that can be caused by hormonal imbalances, obesity, or certain medications. While it can be a source of embarrassment or discomfort for some men, there are various treatment options available, including lifestyle changes, medication, and surgery. By seeking proper diagnosis and treatment, men can overcome the challenges of gynecomastia and enjoy a flatter, more confident chest.